1.怎样判断对象是否可以转换?
可以使用instanceof运算符判断一个对象是否可以转换为指定的类型。
例:
1 public class TestInstanceof 2 { 3 public static void main(String[] args) 4 { 5 //声明hello时使用Object类,则hello的编译类型是Object,Object是所有类的父类 6 //但hello变量的实际类型是String 7 Object hello = "Hello"; 8 //String是Object类的子类,所以返回true。 9 System.out.println("字符串是否是Object类的实例:" + (hello instanceof Object));10 //返回true。11 System.out.println("字符串是否是String类的实例:" + (hello instanceof String));12 //返回false。13 System.out.println("字符串是否是Math类的实例:" + (hello instanceof Math));14 //String实现了Comparable接口,所以返回true。15 System.out.println("字符串是否是Comparable接口的实例:" + (hello instanceof Comparable));16 String a = "Hello";17 //String类既不是Math类,也不是Math类的父类,所以下面代码编译无法通过18 //System.out.println("字符串是否是Math类的实例:" + (a instanceof Math));19 }20 } 程序运行结果:

2.现有三个类
class Mammal{}
class Dog extends Mammal{}
class Cat extends Mammal{}
先对其分别进行初始化:
Mammal m = null;
Dog d = new Dog();
Cat c = new Cat();
下列语句哪一个将引起编译错误?为什么?哪一个会引起运行时错误?为什么?
m = d;
d = m;
d = (Dog)m;
d = c;
c = (Cat)m;
事先判断结果:
出现编译错误:第二行,原因:不能将父类变量赋值给子类变量。
第四行,原因:继承于同一个父类的两个平行子类不能互相赋值。
出现运行错误:第五行,原因:在第一行中,m变量已经指向Dog对象,如果再执行c = (Cat)m,就是让c指向Dog对象,而Cat和Dog之间不存在继承关系,无法让c指向Dog对象。
结论:
对象之间互相赋值时,子类对象可以对父类对象赋值,父类对象不能对子类变量赋值,继承与同一基类的平行子类之间不能相互赋值。
3.运行以下测试代码:
1 public class ParentChildTest { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 Parent parent=new Parent(); 4 parent.printValue(); 5 Child child=new Child(); 6 child.printValue(); 7 8 parent=child; 9 parent.printValue();10 11 parent.myValue++;12 parent.printValue();13 14 ((Child)parent).myValue++;15 parent.printValue();16 17 }18 }19 20 class Parent{21 public int myValue=100;22 public void printValue() {23 System.out.println("Parent.printValue(),myValue="+myValue);24 }25 }26 class Child extends Parent{27 public int myValue=200;28 public void printValue() {29 System.out.println("Child.printValue(),myValue="+myValue);30 }31 } 上边的程序的运行结果是什么?
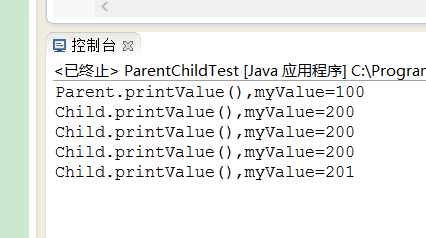
总结:
子类可以赋值给父类,代表父类变量引用子类的对象。子类可以覆盖父类,覆盖后引用的是子类的方法,如果需要引用父类的方法可以用super函数。当子类与父类拥有一样的方法,并且让一个父类变量引用一个子类对象时,到底调用哪个方法,由对象自己的“真实”类型所决定,这就是说:对象是子类型的,它就调用子类型的方法,是父类型的,它就调用父类型的方法。这个特性实际上就是面向对象“多态”特性的具体表现。如果子类与父类有相同的字段,子类方法中访问的是子类中的字段(而不是父类中的字段)。如果子类方法确实想访问父类中被隐藏的同名字段,可以用super关键字来访问它。如果子类被当做父类使用,则通过子类访问的字段是父类的。